Mold Library
Aspergillus fumigatus
Distribution
Aspergillus fumigatus is ubiquitous, reported from a wide range of substrates such as soils, plants, seeds, sludge, wood chips, compost, cotton, and excreta of birds. Aspergillus fumigatus is abundant on rotten plant material at higher temperatures and in air during biological waste treatment.
Growth Characteristics
Aspergillus fumigatus grows well over a wide temperature range (up to 57oC).
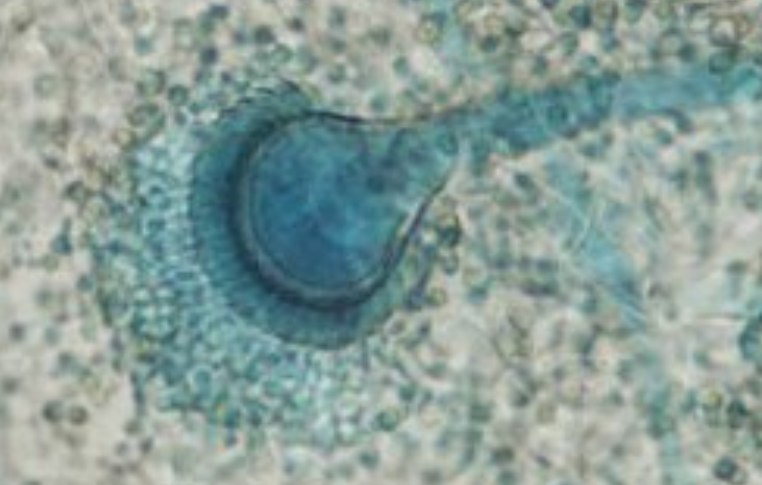
Microscopic Characteristics
Aspergilli uniseriate. Stipe uncolored, smooth-walled. Vesicle pyriform. phialides cover upper half to two-thirds of the vesicle. Conidia globose, smooth to finally roughened.
Health Effects
Aspergillus fumigatus is a human and animal (pets like dogs and cats) pathogen. Some of the allergies and diseases it may cause include: asthma, rhinitis, farmers lung (allergic alveolitis), hypersensitive pneumonitis, invasive disseminated aspergillosis, allergic fungal sinusitis (which may lead to fungal balls or become invasive; may cause cranial life - threatening complications).
Aspergillus fumigatus may also cause infections such as keratitis and organ infection inindividuals with compromised immune response. Such infections can affect the skin, eyes, lung, and/or other organs and systems. A. fumigatus may also cause nosocomial infections in immunocompromised patients. Some toxins associated with Aspergillus fumigatus include: fumitotoxin, chanoclavine, tryptoquivalins, fumitrimorgins, verrucologen, Ergot alkaloids, and fumigatoxins.