Mold Library
Aspergillus
Distribution
Aspergillus is a cosmopolitan fungus with a worldwide distribution. Aspergillus is often isolated from soil and plant materials, particularly in tropical and sub-tropical regions. Aspergillus spores are generally air dispersed.
Growth Characteristics
Aspergillus species range in growth from relatively slow growing to fast growing. Colonies are often green but can range in color from white (i.e. A. candidus) to brown or black (i.e. A. niger). Some Aspergillus colonies may appear yellow, pink or red in color as well.
Microscopic Characteristics
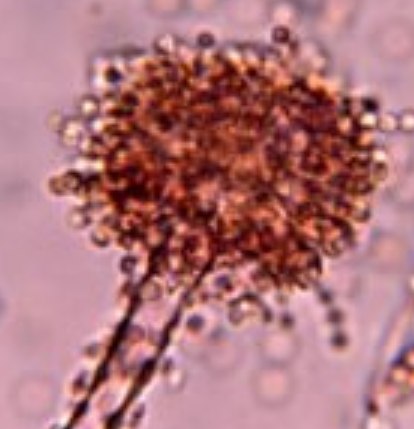
The microscopic structures of Aspergillus species generally have the same features. A stipe, which is similar to a palm tree's trunk; a vesicle, similar to the palm tree's top where the fronds branch out; the phialides, which are like the stem of the palm fronds; and finally the spores (or conidia), which can be related to the frond themselves. The spores, unlike a palm's fronds, however, develop in chains. Spores range in shape from spherical to ovate and ornamentation varies from smooth to spiny or roughened.
Health Effects
A number of Aspergillus species have been recognized as agents in human mycoses. The most common species implicated are A. flavus and A. fumigatus. Aspergillus species are common allergenic agents and can also cause invasive disease.