Mold Library
Bipolaris
Distribution
The genus Bipolaris has a worldwide distribution. Bipolaris species include saprobes and pathogens. They are pathogens of numerous species of plants, particularly grass, and Bipolaris is also known to occur in soils and decaying foods (e.g. grains).
Growth Characteristics
Bipolaris has a rapid growth rate. The colonies of Bipolaris are generally white in color initially changing to a dark olive to black. Colony texture is generally downy or velvety.
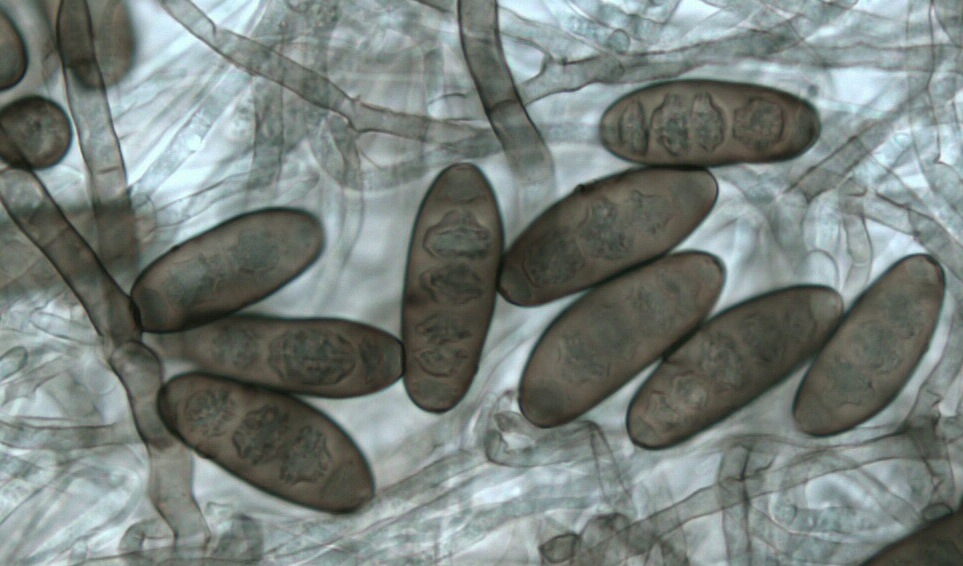
Microscopic Characteristics
Both the hyphae and the spores of Bipolaris have a brown to red pigmentation. The spores of this genus are rather unique in that they typically contain 3 to 6 cells that are horizontally partitioned by septae. Germination of the spores occurs from the two terminal cells, hence the name Bipolaris. The reproductive hyphae (conidiophores) have a zig-zag appearance on which the spores arise on each zig and zag.
Health Effects
Bipolaris has been known to be an allergenic irritant, cause pneumonia, dermatitis, and fungal sinusitis. There also reported instances of infection of the eye's corneas, and of the lungs (particularly upper respiratory tract). Various species of this fungus can produce the mycotoxin serigmatocystin, which in the past has been known to cause liver and kidney damage when ingested by animals in laboratory settings.