Mold Library
Cladosporium
Distribution
Cladosporium is a ubiquitous fungus with a world-wide distribution. It is commonly isolated from soil, plant debris, leaf surfaces, textiles, food, lumber and other building materials, and is often the most frequently isolated mold in air samples from both indoor and outdoor environments. Cladosporium prefers areas with free water or high humidity and is frequently found in water-damaged homes.
Growth Characteristics
Cladosporium is relatively slow-growing. In culture, colonies are characterized by a velvety texture, a dark olive-brown to brownish-black in color with a black reverse, and a distinct margin. On building materials, Cladosporium growth generally appears as olive-brown to black.
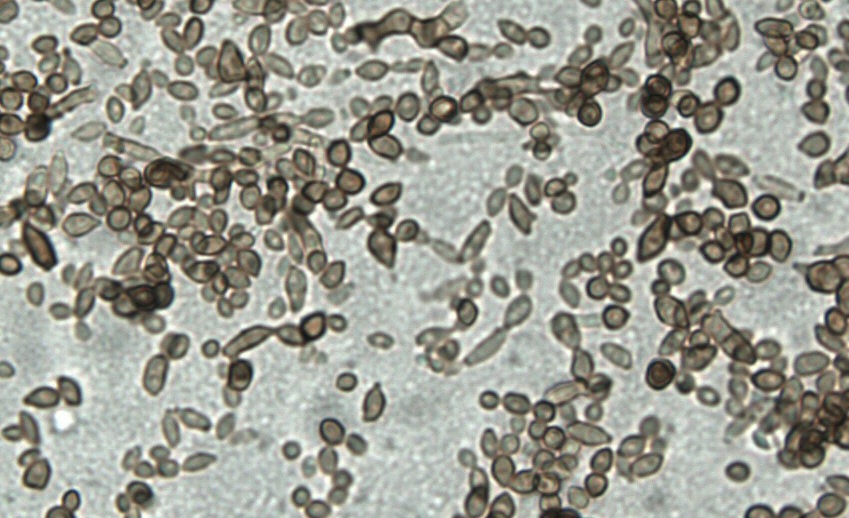
Microscopic Characteristics
Blastoconidia are produced in fragile, branching chains on an erect, pigmented condiophore. Condia are brown, smooth or rough-walled, 1-4 celled, shield-shaped at base of chain, oval to round at tip of chain, and are characterized by prominent scars at detachment points.
Health Effects
Cladosporium is a common allergen. Although no species of Cladosporium is considered directly pathogenic to humans, rare cases of opportunist infections in immunocompromised hosts (i.e. patients with leukemia, AIDS and other autoimmune disorders) have been reported. Cladosporium species are reported to cause superficial and subcutaneous skin infections. Cladosporium is not known to produce significantly harmful mycotoxins.